タイ科
タイ科(Sparidae)

81 ヨーロッパマダイ(Yooroppa-madai)
Pagrus pagrus (Linnaeus, 1758)
Common seabream (En.); Pagre commun (Fr.); Pargo (Sp.); Besugo, Pargo colorado (Arg., Urg., Ven.); Pagro (Br.)
特 徴:
背鰭12棘,10軟条,臀鰭3棘,8軟条,胸鰭15~16軟条,腹鰭1棘,5軟条,鰓耙数6~7+9~11,側線鱗数53~57。体長に対する体高の割合は40.5~42.4%,頭長は31.3~33.3%,眼径は7.3~8.2%,両眼間隔は8.8~9.6%,吻長は13.4~14.7%,上顎長は12.4~12.9%,尾柄高は9.6~9.9%,胸鰭長は34.1~36.7%,腹鰭長は18.8~23.8%。体は他のマダイ類に比べやや低い。頭の上部外郭は眼前部でわずかに隆起し,吻部から前下方へ急傾斜する。両眼間隔域はやや広い。鰓耙は長く,わずかに扁平。上顎の前部に4本,下顎に6本の犬歯がある。両顎の側部には2列の臼歯があり,それぞれ前方に数本の円錐歯があり,後方にやや強い数本の臼歯が並ぶ。眼は眼下幅よりもわずかに大きい。鱗はやや大きく弱い櫛鱗。胸鰭は臀鰭第2棘に達する。腹鰭は肛門にわずかに達しない。一般に臀鰭の第3棘は第2棘よりも長い。体は赤色で,側線上には体背部外部に平行でやや不規則な,側線下には体軸に平行に縦走する青緑色小点が散在して並ぶ。尾鰭は赤く,その縁辺は半透明。他の鰭は淡赤色。
分 布:
地中海,英国からセネガルまでの東大西洋,アメリカの南岸からブラジル,アルゼンチンの北部までの西大西洋に分布する。アルゼンチンでは北部のラプラタ河口沖からマルデルプラタ付近までの沿岸域に分布する。
備 考:
本種は背鰭棘条部中央下の横列鱗数5 1/2であることで,マダイ属の他の種から区別される。学名としてPagrus unlgarisが用いられる場合もあるが,赤崎(1962)に従った。体長は通常,約20~50cm。最大体長75cm(Quignard, 1973)。
(稲田伊史)
Material examined:
3 from Argentina (193-231 mm SL), FSFL EL 768; EM 231, 302.
Description:
D ⅩⅡ, 10 A Ⅲ, 8; P1 15-16; P2 Ⅰ, 5; GR 6-7+9-11; LLS 53-57. HL 31.3-33.3% of SL; ED 7.3-8.2; BD 40.5-42.4; SN 13.4-14.7; IO 8.8-9.6; UL 12.4-12.9; CP 9.6-9.9; P1L 34.1-36.7; P2L 18.8-23.8.
Body oval, head large, its anterodorsal profile steep, especially in young specimens. Body low compared with other sparids. Eye moderately large, placed near dorsal profile of head; eye diameter slightly less than 2 times in preorbital length; slightly larger than suborbital width. Interorbital width wide. Gill-rakers long, little flattened. Jaws bearing 4 to 6 pointed and curved teeth (canines) anteriorly, followed by conical teeth and then by molars (rounded teeth). Scales large, weak ctenoid. Tip of pectoral fin reaching to 2nd spine of anal fin. Pelvic fin hardly reaching to anus. Third spine longer than 2nd spine in dorsal fin.
Distribution:
Common in the Mediterranean. In the eastern Atlantic coasts it is found from the British Isles to Senegal, rare from Spanish coast nothward. In the western Atlantic coasts it is found from south coasts of U. S. A. to Brazil and northern part of Argentina. In Argentina, it is distributed from La Plata River to Mar del Plata.
Remarks:
This species differs from other Pagrus by 5 1/2 number of transverse rows of scales under the midpart of first dorsal fin. Sometimes Pagrus vulgaris has been used, but we follow Akazaki (1962). Body length is usually from 20 cm to 50 cm and the maximum length is 75 cm (Quignard, 1973). Lives over gravel bottoms, in the vicinity of seaweeds and beds of higher aquatic plants and around rocks, down to depths of about 60 m. Feeds on fishes, crabs and shrimps. Large individuals take also cephalopods and other molluscs in the case of the Mediterranean population (Quignard, 1973).
(Tadashi INADA)
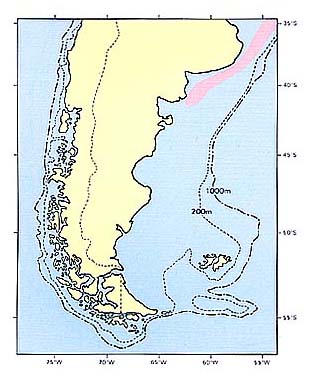
Distribution of Pagrus pagrus in Patagonia.
- 1